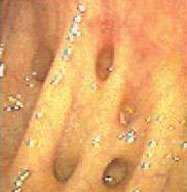
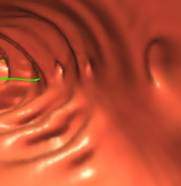
Virtual Colonoscopy definition - The computerized rendering of CT data into a format, which mimics the visualization (virtual reality) of the colon obtained from within by gastroenterologists using an endoscope (fiberoptic tube with a camera at its end).
Preliminary results of the National CT Colonography Trial (ACRIN 6664), a study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and performed on 2,531 participants in 15 U.S. centers, yielded an impressive per-patient sensitivity of 90% for adenomatous colorectal lesions 1 cm or larger in diameter, a sensitivity on par with that of optical colonoscopy.
A large multicenter trial of 1233 patients at low risk for colon cancer has now shown that the Viatronix software allows a radiologist using a primary 3D interpretation to have accuracy similar to optical colonoscopy.
Computed Tomographic Virtual Colonoscopy to Screen for Colorectal Neoplasia in Asymptomatic Adults. NEJM
Pickhardt P. J., Choi J. R., Hwang I., Butler J. A., Puckett M. L., Hildebrandt
H. A., Wong R. K., Nugent P. A., Mysliwiec P. A., Schindler W. R.
Colorectal cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in the United States with 130,200 newly diagnosed cases and 56,300 deaths in 2000. 152,000 newly diagnosed cases and 57,000 deaths in 2002 are predicted (American Cancer Society statistics). Since it takes up to 10 years for a colonic polyp to grow to a size with a high likelihood of invasive cancer, timely and accurate patient screening with subsequent polyp removal can prevent over 90% of malignant colorectal cancers.
As a result, recommendations have been made for large scale screening programs for persons beginning at the age of 50 (American Cancer Society/ACS). Colorectal cancer screening guidelines given in the journal Gastroenterology in 1997 suggest that the screening modality must be safe, available, acceptable to the patient and cost effective. In March, 2000, the ACS recommended fecal occult blood testing every year, optical sigmoidoscopy every 5 years, or complete evaluation of the colon with air contrast barium enema or optical colonoscopy every 10 years. More recently published articles in the New England Journal of Medicine in July, 2000 showed that both air contrast barium enema and sigmoidoscopy are not very effective screening tests because they both miss more than 50% of colonic polyps, while sigmoidoscopy would miss more than 52% of proximal cancers. Thus optical colonoscopy is now the only established effective method of colon cancer screening. Polyps can be removed and thereby decrease the chance of subsequent development of colon cancer. It however, does not satisfy the previously mentioned screening criteria in that many patients and physicians avoid it, it is expensive, carries a risk of perforation and even death.
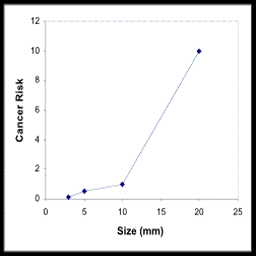
These facts and advancing computer technology have advanced virtual colonoscopy into the forefront of colon cancer screening. The medical literature in this new screening technique is still limited, has shown varying accuracy, but clearly has shown an improving trend as radiologists gain experience and computer technology improves.
H. Fenlon et al. (Boston U) NEJM Nov, 1999
100 patients at risk for neoplasm with 115 polyps and 3 carcinomas
All polyps - sensitivity 82%, specificity 84%
1 to 5 mm (53) - 55%
6 to 9 mm (40) - 82%
10 mm or larger (22) - 91%
Better sensitivity with adenomas (91%) than hyperplastic polyps (71%)
Picker Voxel workstation – 1996 technology
McFarland, E et al (Mallinckrodt) Radiology – Feb 2001
Assess performance and reader agreement of 2D and 3D techniques using Vital Images, Vitrea 1.1
Similar performance between 2D multiplanar reformation (MPR) and 3D display
3D showed improved characterization in individual cases
Yee, J (UCSF – VA) Radiology - June 2001
300 patients with CT colonography and OC 96/300 (32%), screening 204/300 (68%) symptoms
Initial review of magnified 2D CT images followed by flythrough using GE Navigator
Overall sensitivity for polyp detection: 90.1% Overall specificity : 72.0%
Conclusion: CT colonography comparable to standard colonoscopy
94% sensitivity to detect adenomas 10mm or larger (Back to back OC misses 6% of adenomas 10mm or larger)
Comparable performance in the screening and symptomatic groups 87% of false positive lesions were smaller than 10 mm.
Inadequate bowel cleansing strongly related to more false-positive polyps
Poor colon distension related to increase in number of false-negative polyps
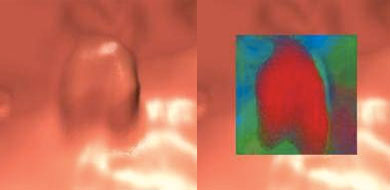
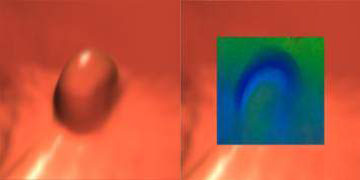
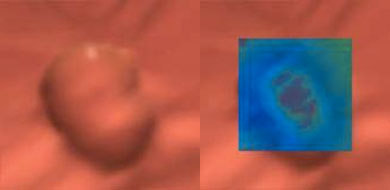
Pseudopolyp on virtual view (left), shown to be stool ball on translucency view (right)
The preliminary data (unpublished at this time) from Stony Brook show excellent sensitivity and improved specificity compared with previous publications.
Stony Brook Clinical Studies
(using earlier version of) Viatronix software with primary 3D interpretations - 62 patients with both virtual and optical colonoscopy comparison
3 - 4 mm: virtual 5, optical 4
5 - 9 mm: virtual 12, optical 9
10+ mm: virtual 7, optical 7
Boca Raton RegionalHospital is pleased to be working with the latest technology created by Viatronix in combination with advanced multi-array CT scanners enabling faster image acquisitions with much thinner section intervals than what has been previously published. The procedure is summarized below:
Potential Advantages of Virtual Colonoscopy - Accurate detection of 4mm or larger polyps - Non-invasive with virtually no risk - Significantly less expensive - Time efficient examination - patients can work the same day as procedure - Flexible viewing and analysis - Record: 3D electronic model
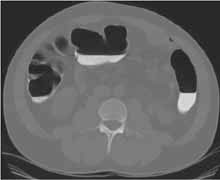 Multi-array CT Scanner Data Acquisition Colon inflated with CO2 Two 15 Sec Helical CT Scans Of Patient's Abdomen in supine and prone positions
500 slices at 800 micron intervals per data set
Multi-array CT Scanner Data Acquisition Colon inflated with CO2 Two 15 Sec Helical CT Scans Of Patient's Abdomen in supine and prone positions
500 slices at 800 micron intervals per data set
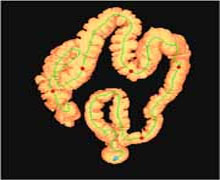 Automatic Post-processing Segmentation, electronic cleansing Transfer to Viatronix computer Reconstruction of 3D Colon Model with electronic Cleansing
Automatic Post-processing Segmentation, electronic cleansing Transfer to Viatronix computer Reconstruction of 3D Colon Model with electronic Cleansing

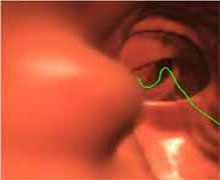 Visualization Automatic or Interactive Navigation Inside Colon 2D and 3D
Visualization Automatic or Interactive Navigation Inside Colon 2D and 3D
Supine and Prone Imaging Improved colonic distension of dependent segments
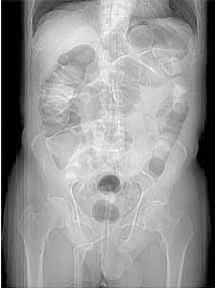
Supine
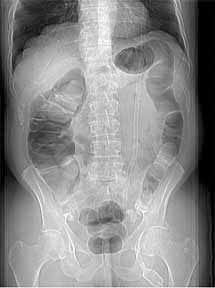
Prone
Call : (561) 955-4700
