At the time of scheduling the patient will be asked a series of questions including symptoms, prior history of heart disease and interventions, which will allow us to tailor the examination to answer all of the relevant questions that the referring physician may have. Also, we will need to know if the patient suffers from significant cardiac arrhythmias, which may compromise the quality of the images and diagnostic efficacy.
At the time of the patient's arrival in our department, the patient will be fully assessed by a cardiac trained nurse (BLS/ACLS certified). The patient's heart rate, blood pressure, ECG, and history will be reviewed. An intravenous line will be placed into the patient's arm for fluids and medication. If not contraindicated, we generally administer medications to slow the patient's heart rate (generally beta-blockers), which improves the image quality and helps ensure a diagnostic study. We will particularly need to know if the patient suffers from asthma or bronchospasm. If beta-blockers cannot be administered, other medications may be used. When the patient's heart rate is slow and stable, the CT examination is performed which only takes a few minutes including the placement onto the table and the actual image acquisition (done in a breath hold in just seconds). After the examination, the patient is monitored for a short period in our department before discharged.
The test requires lying still in one of our short bore magnets (which are less claustrophobic than older generation systems) with ECG monitoring leads and surface RF antenna coil placed on your chest. There will be a vibrating noise, which may be loud during the imaging sequences. The technologist will be in constant visual and auditory communication with you during your examination and can pause the examination if necessary. You will be asked to hold your breaths for periods of time ranging from a few seconds to as long as 20 seconds. Please let the technologist know if you cannot hold your breath and different sequences will be used. After the examination, you will be monitored for a short period in our department before discharged.
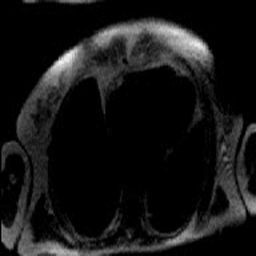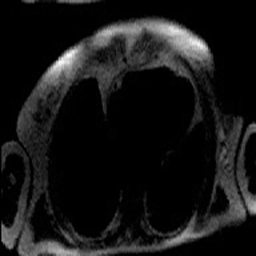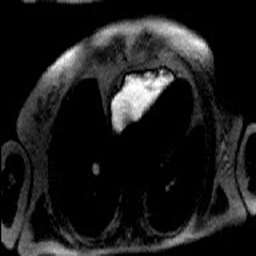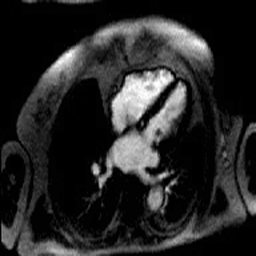
Visualization of cardiac and other structures – because the MRI/MRA data can be obtained with differing tissue contrast, in any plain and even volumetrically, exquisite structural detail is now possible. Post processing and advanced visualization algorithms allow the extraction of specific structures such as structures and tumors within or near the heart, blood vessels and soft tissue structures, which allows the physician to better understand complex anatomy. This can be invaluable to surgeons in their preoperative planning and very useful in training.
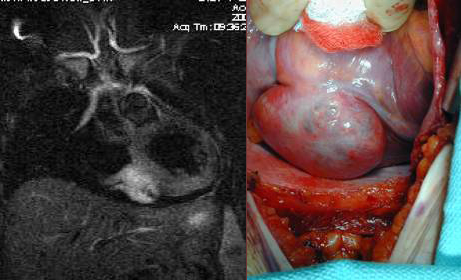
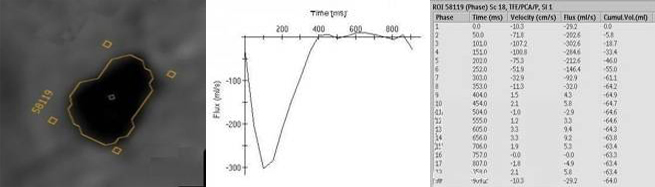
Visualization of wall and valve motion– The MRI data is acquired synchronized to the cardiac cycle and can be acquired in any arbitrary plane in three-dimensional space during multiple phases of the cardiac cycle. The cardiac function can be assessed non-invasively (like echocardiography). Precise quantitative calculation of ejection fraction can be obtained from these data sets as well as qualitative evaluation of wall motion and valve function. Cross sectional anatomic evaluation of valves with phase velocity mapping to quanititatively measure stenotic and regurgitant jets is now routine thereby clarifying and or confirming findings already noted on echocardiography. This may obviate the need for cardiac catheterization, which currently serves at most institutions as the final preoperative test before valve replacement and ventricular reduction surgery.


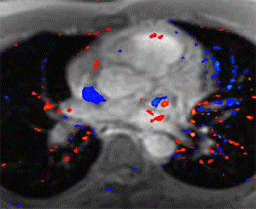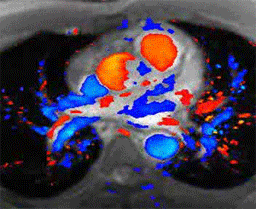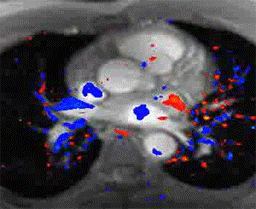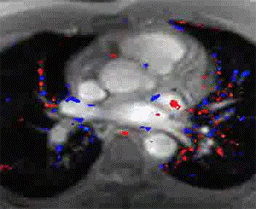
Cardiac nuclear medicine and stress testing has been used since the 1970's and is well established as a useful test for the non-invasive detection of high grade coronary artery blockages and assessing the heart's physiologic response to stress. It is widely available and can be performed in an out patient setting. It is however limited in its sensitivity and specificity with as many as 30% of patients being falsely reassured that they have no significant coronary artery disease and some being unnecessarily alarmed with equivocal results or falsely positive results leading to an unnecessary cardiac catheterization.
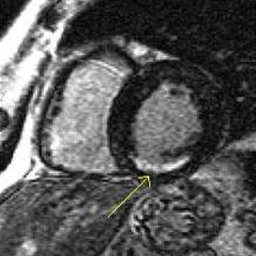
Cardiac MRI stress testing is generally performed within hospitals and is combined with a comprehensive MR examination which also assesses wall and valve motion as well as viability with breath hold sequences designed to detect evidence of previous myocardial infractions (heart attacks) which are often missed by other traditional modalities.
The patient is imaged at rest using cine and perfusion sequences and also again during pharmacologic stress using intravenous Adenosine infusion during blood pressure and ECG monitoring. Because of MRI's superior spatial and temporal resolution compared with nuclear medicine, the sensitivity and specificity in detection of high-grade blockages of the coronary arteries is significantly greater with MRI and felt to be at least in the 85-90% range. Also, occult previous infarctions are often visualized which can also non-invasively confirm coronary artery disease.
MR angiography (MRA)- he most exciting forefront of research is reliable non-invasive direct imaging of the coronary artery lumen and plaque in the vessel wall, which is now possible with 64 slice cardiac CT. While MRA can visualize the coronary arteries in some patients and can reliably exclude proximal narrowing, it is not routinely used for this purpose. New research protocols include: navigator sequences to suppress motion artifacts, newer injectable contrast agents to increase the signal of blood thereby boosting the signal/noise and potential spatial/temporal resolution, as well as newer parallel imaging techinques, may ultimately make coronary MRA a clinical reality. Current research in animal models also includes continuing improvements in data acquisition and visualization which allows following the type and distribution of the plaque while testing newer liped metabolism drugs to treat atherosclerosis. Patients who have already undergone revascularization procedures including stenting and bypass are not good candidates due to the metallic artifacts, which degrade the MRI images.
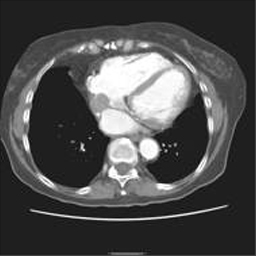
The common use of MRA is the non-invasive visualization of larger vessels in the chest including the thoracic aorta and pulmonary arteries. A rapid bolus injection of gadolinium can be used to enhance speed and quality of the visualization making it possible to reliably diagnose aneurysms, dissections, and thrombus formation. Also, complex anomalies of the heart and blood vessels can be fully assessed with MRI/MRA. The most common cardiovascular application of MRA is pretreatment planning of carotid artery blockages.
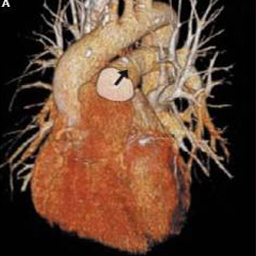
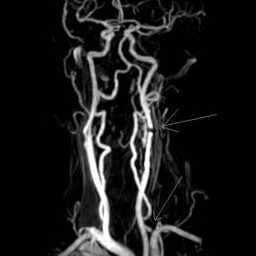
The Holy Grail is a comprehensive MRI/MRA examination of the heart and blood vessels to answer all of the common clinical questions including the diagnosis of:
Undoubtedly CT and MRI will change the paradigm of cardiac imaging forever and cardiac catheterization will become a primary therapeutic procedure.